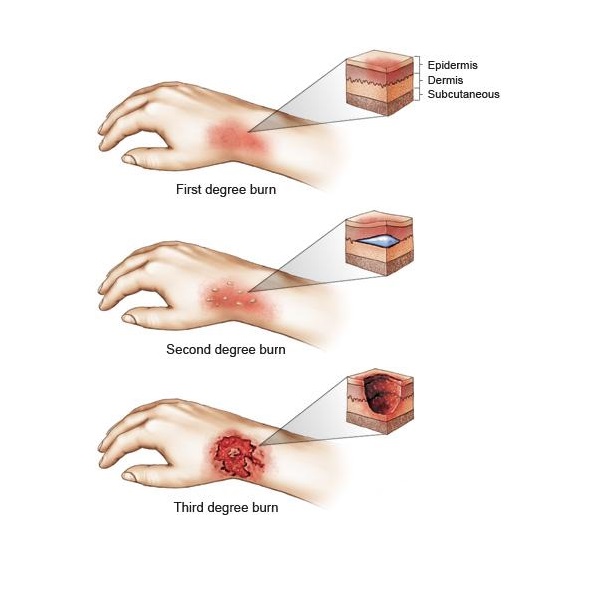
Degrees and level of burns
Burns include three types of first degree, second degree and third degree burns. The degree of burn is determined by the damage to the skin. For example, first degree burns are the least serious and third degree burns are the most serious. In general, there are different types of burns: first-degree burns (red skin without blisters), second-degree burns (blisters and thickening of the skin), third-degree burns (high thickness with white and leathery skin); , and fourth-degree burns. This type of burn includes the symptoms of third-degree burns and extends from the skin to tendons and bones.
1st degree burn
First degree burns are usually minimal and affect only the outer layer of the skin. which is considered the most common type of inflammation, most sunburns fall into this group. 1st degree burns cause minimal skin damage. They are also called “dermatitis” because they affect the outer layers of the skin.
1st degree burn symptoms
Symptoms of a first-degree burn include redness, mild inflammation or swelling, pain and dryness, and peeling of the skin as it heals. Since this inflammation affects the top layer of the skin, once the skin cells are removed, the signs and symptoms disappear. First-degree burns usually heal without scarring within 7 to 10 days. If there is inflammation in a large area of skin greater than 3 inches on the face or large joints, including the knees, ankles, feet, spine, shoulders, elbows, and forearms, you should see a doctor. First-degree burns are usually treated with home care. The recovery period may be shorter than the burn time.
1st degree burn recovery method
- Put the burn in cold water
- Use of acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Using lidocaine medicine along with aloe vera gel on the wound
- Use of antibiotics and loose gauze to protect the affected area
2nd degree burn
Second degree burns are more severe and involve the outer layer of the skin and the next layer, the dermis. Their recovery time is longer and more difficult. This type of burn causes scars on the skin and is very red and painful. Some blisters break open, giving the burn a wet, moist appearance. Over time, thick, soft, or hard tissue may form in the wound. Due to the sensitivity of these wounds, the affected area should be kept clean and properly bandaged to prevent infection. Helps heal burns faster.
2nd degree burn treatment duration
Some second-degree burns take more than three weeks to heal, but most heal within two to three weeks without scarring, but often with changes in skin pigmentation. The worse the blister, the bigger the burn. In some severe cases, a skin graft is required to repair the damage. Skin grafting takes healthy skin from another part of the body and transfers it to the burned skin area.
The treatment of partial second degree burns is as follows
- Put the skin in cold water for 15 minutes or more.
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
- Using antibiotic cream to treat blisters.
However, if the burn involves a large area, such as the face, hands, buttocks, groin, or legs, seek immediate medical attention.
3rd degree burn
Third degree burns are one of the most serious types of burns. which affects both layers of the skin and can also affect other tissues such as sweat glands. Third degree burns usually require skin care and surgery. Apart from fourth degree burns, third degree burns are the most serious. They cause the most damage and spread in every layer of the skin. Contrary to this misconception, third degree burns are not more painful. But in this type of burn, the damage is so great that there may be no pain due to nerve damage. Third-degree burns heal without surgery, with severe scarring and excess flesh.
Duration of healing wounds from 3rd degree burns
There is no specific time to treat these wounds. Severe burns can also cause fatal complications. Normally, the body mounts an inflammatory response to protect itself from injury, infection, or other threats. But in some cases, such as a severe burn, the body overreacts and the inflammatory response can cause further damage. In general, shock causes damage because the intense inflammatory response causes a lack of oxygen in tissues and organs. Many organs in the body, such as the lungs, heart, and brain, may burn due to shock damage.
The main concern in 3rd degree burns
Infection is another major concern with third-degree burns. Severe skin damage exposes the body to pathogens. Burns can also weaken the immune system, meaning the body is less able to fight infections. In particular, pneumonia and sepsis infections are common and potentially fatal complications.
Tetanus is another potential complication of burns
Tetanus is another potential complication of burns on all surfaces. Like sepsis, tetanus is a disease caused by bacteria. It affects the nervous system and eventually leads to muscle contraction problems. As a general rule, everyone in your family should get a tetanus checkup every 10 years to prevent this type of infection. Severe burns are associated with the risk of hypothermia and hypovolemia. A dangerously low temperature defines hypothermia. Although this may seem like an unexpected burn problem, it is actually caused by excessive body heat loss due to injury. Hypovolemia, or low blood volume, occurs when your body loses too much blood due to a burn.




بدون دیدگاه