Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s defense mechanism. Therefore, inflammation occurs in the body when bad stimuli enter the body. Inflammation is a local reaction that occurs after tissue damage in the body such as pain, redness, swelling and heat to fight pathogens. In fact, inflammation is a protective mechanism that occurs after a scratch, cut, burn or any type of tissue damage and causes swelling, redness, heat and itching in the affected area. The causes of inflammation can be microbiological (bacteria, viruses, fungi) or chemical (allergens, etc.) or physical (burning, heat, ionizing light, UV light, etc.). Inflammation can also occur after autoimmune reactions. The body tries to remove harmful substances and repair the damage through inflammation.
Mechanism of inflammation
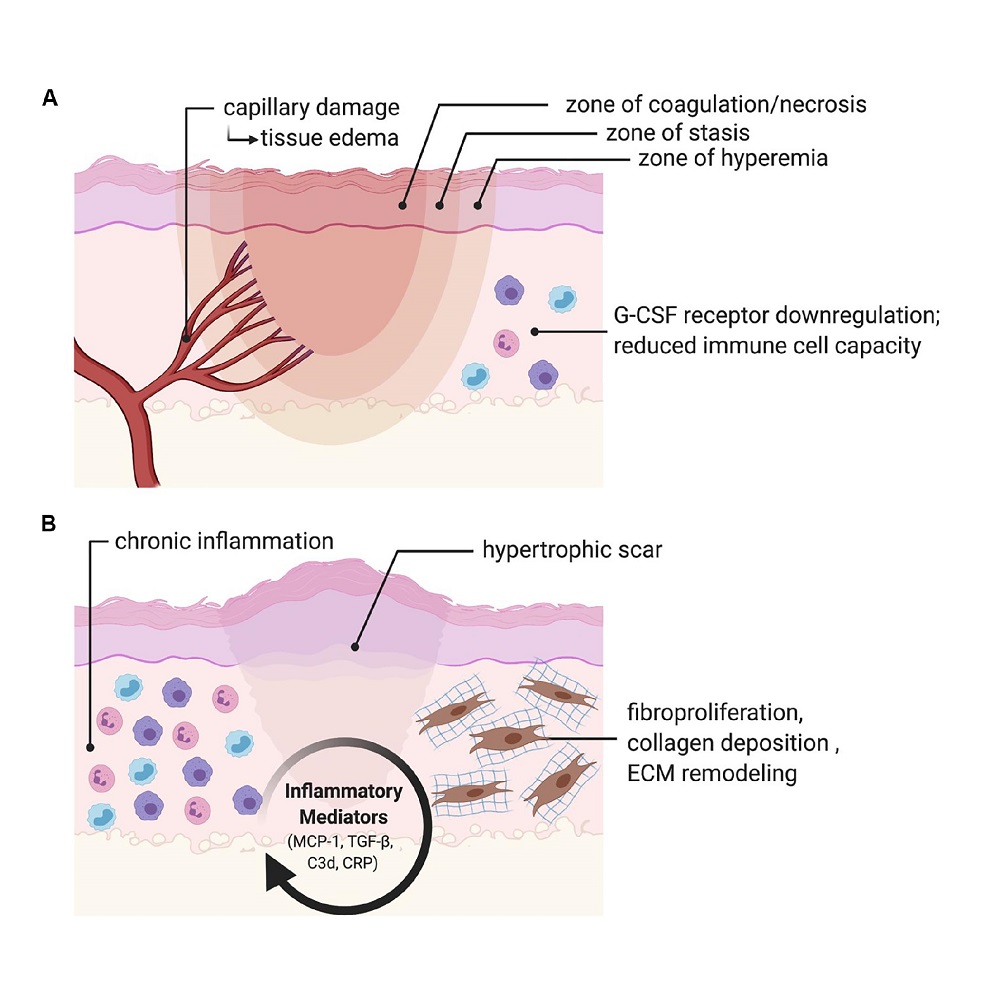
The mechanism or inflammatory process is that the damaged area is separated from the rest of the cells. Then tissues and lymph nodes in the inflamed area are closed with blood fibrinogen, and thus water does not flow in this area. The wall of this damaged area slows down the spread of bacteria or toxic products. This action slows the spread of bacteria or toxic products in the area. The small blood vessels that deliver blood to the tissue capillaries dilate and the blood flow to the tissue increases. Then the capillary permeability increases, so water and blood proteins leave the capillaries and enter the intercellular space.
The end of the inflammation mechanism pathway
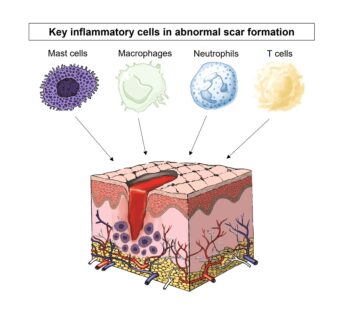
In the mechanism of inflammation, finally, groups of white blood cells that play a role in the immune system (neutrophils and macrophages) leave the capillaries and reach the intercellular space. Neutrophils are a group of white blood cells that destroy invaders by releasing proteins called enzymes, and macrophages are cells that eat invaders.
The end of the inflammation mechanism
Termination of the Mechanism of Inflammation This physiological response, which occurs rapidly, is terminated by appropriate care. Cold packs can be used to reduce heat and inflammation. Also, as a home remedy, inflammation caused by burns can be reduced using potatoes. Raw potatoes have anti-inflammatory properties and can reduce inflammation and blisters. And it helps as a pain reliever. This treatment is very useful for minor skin burns.
Some useful treatments to resolve inflammation mechanism
Aloe vera gel can be used in first and second degree burns to increase blood circulation and inhibit the growth of bacteria to eliminate the inflammation mechanism. Using honey as well as tea can be useful because of their anti-inflammatory properties. In more severe and widespread cases, you should consult a specialist and possibly take antibiotics. Anti-inflammatory drugs include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a class of drugs used to treat pain, fever, and inflammation. This drug category includes 5 to 10% of prescription drugs annually. These drugs do not contain steroids, so they are called non-steroidal.
Consequences of negligence
Inflammation is actually tension that informs a person that a part of the body is damaged. And sometimes the immune system alone is not able to cope with the damage. If the inflammation is not removed or reduced, the immune system weakens and the inflammatory agent spreads. As a result, the adjacent cells are also infected and destroyed. You may even lose a piece of tissue. As the injury process continues, inflammation and damage can get out of control and leave irreparable and lasting damage. This recovery process will be long and difficult. As a result of burns and at a temperature above 44 degrees, proteins lose their three-dimensional shape and are destroyed. This action causes tissue damage.
Direct effects of burns
Many of the direct effects of burns disrupt the skin’s normal function, and these effects destroy the skin’s ability to prevent water loss and regulate body temperature. As a result, the rupture of the cell membrane causes the release of potassium into the intercellular space and instead the absorption of water and sodium, which causes significant inflammation, a reaction that causes capillary dehydration and edema. This process causes total blood loss. In this case, the remaining blood loses a large amount of plasma and the blood concentration increases.
Consequences of not stopping the inflammation mechanism
1 If the inflammation is not stopped, blood flow to organs such as the kidneys and digestive system is reduced, which can lead to kidney failure and stomach ulcers. And the continuation of this process can lead to an increase in the body’s metabolism, which, if not treated, can continue for years and lead to heart failure and weakening of the body’s defense system.




بدون دیدگاه